Case : South Korea
What effects that gaming culture has on the members of its society;
Gaming addiction vs gaming professionalism
How serious is gaming addiction?
According to the Washington Post, 2.4% of South’s Korea’s population aged 9-39 suffers from gaming addiction. Another 10.2% are considered to be borderline cases.
In 2005 alone, ten people died from game addiction related causes.
A couple in Incheon, Korea was arrested in June 2005 when they left their 4-month old daughter alone at home for five hours while going to play World of Warcraft at a PC Baang(Internet café). The baby died of suffocation from turning over on her stomach while the parents were gone.
A number of reasons are blamed for the rise of online gaming addiction in South Korea. They range from the longer amount of time needed to finish extensive gaming objectives or storylines, to inexpensive Internet access (averaging $30.00 a month for household high-speed Internet services), to a society used to living in small apartments or homes trying to escape unfulfilling daily lifestyles.
The Washington Post says, “Gaming addiction is in part because young people here suffer from acute stress as they face educational pressures said to far exceed those endured by their peers in other countries. It is not uncommon, for instance, for South Korean students to be forced by their parents into four to five hours of daily after-school tutoring. With drug abuse and teenage sex considered rare in the socially conservative country, escape through electronic games can be a huge attractive outlet.”
What is addiction?
Addiction is currently defined as a behavior over which an individual has impaired control with harmful consequences (Cottler, 1993; Rounsaville et al.,1993 in Robert West, 2001). Thus, individuals who recognize that the behavior is harming them or those whom they care about find themselves unable to stop engaging in the behavior when they try to do so (Heather, 1998 in Robert West, 2001). The severity of the medical, psychological and social harm that can be caused by addiction, together with the fact that it violates the individual's freedom of choice, means that it is appropriate to consider it to be a form of psychiatric disorder: a disorder of motivation (Robert West, 2001).
Addiction typically involves initial exposure to a stimulus followed by behaviors seeking to repeat the experience. After a number of repetitions of the behavior-stimulus sequence, the addiction becomes established.
The starting point for a view of addiction as excessive appetite is that there exists a range of objects and activities which are particularly risky for humans, who are liable to develop such strong attachment to them that they then find their ability to moderate their behavior significantly diminished.
Addiction, as an attachment to an appetitive activity, so strong that a person finds it difficult to moderate the activity, despite the fact that it is causing harm (Jim Orford, 2001).
What are the signs of gaming addiction?
- PC/Video game use characterized by intense feelings of pleasure and guilt.
- Obsessed and pre occupied about being on PC even when disconnected.
- Hours playing increasingly, seriously disrupting family, work, social life.
- Lying about PC Game use.
- Feelings of withdrawal, anger depression when not on or when uninvolved with game.
- Large phone or credit card bills due to online services.
- Fantasy life replaces emotional life with partner.
The South Korean government, in support of fighting game addiction, has taken several steps:
The Korean Agency for Digital Opportunity & Promotion operates centers where people can go to for help on gaming and internet addiction. In 2003, its forty centers counseled 2,243 people. In 2004, KADO counseled 8,978 people. Over 10,000 people were admitted to therapy programs in 2005. KADO’s programs consist of alternative recreational programs and group therapy.
South Korea’s Ministry of Information and Communication is also opening similar centers at universities and is funding anti-addiction courses at South Korea universities.
Not all intense gaming is a bad thing. A few intense gamers put their time in, and it becomes a successful venture for them: professional gaming. South Korea’s government is helping fund construction of the World’s first e-sports stadium, to be completed in 2008, where big screens will soon display big competitions.
Can gaming creat new revenue sources and have positive impact to its society?
The most successful professional gamers in South Korea are currently playing Starcraft, FIFA Series, and Warcraft Ш. Fewer than twenty players in the Korean Pro-Gamer Association make six figures a year, while about fifty out of its total 170 members make $40,000-$60,000.
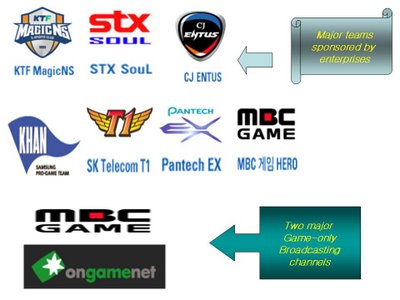
Two cable TV networks, known as Ongamenet and MBCgame, compete for viewers with their own 24-hour programming dedicated to PC, console gaming and both cover South Korea’s professional gaming scene. Fierce gaming competitions are held, backed by major corporate sponsors such as SK Telecom’s T1, KTF’s Magicns, Pantech’s EX, CJ’s Entus, Samsung’s Khan and STX’s Soul providing interactive benefits for the team as well as for the enterprises’ name recognition. Game studios overflow with live audiences trying to catch a glimpse at players who are practically given celebrity status
Ongamenet, a 24-hour PC/console gaming cable channel. Their number one program is called Ongamenet Starleague, which is a three-month long Starcraft tournament broadcast live every Friday beginning at 7:00pm. Players in the final round compete for a top cash prize of $80,000. Second and third place winners can win up to $50,000 and $30,000, respectively.
Sky Proleague is a year long, with eleven Starcraft teams, eleven rounds, and a $100,000 dollar ultimate prize. Over 120,000 spectators attend the final match. It has four studio facilities, and is in the top twenty channels watched out of South Korea’s ninety-nine cable TV channels.
MBCGame covers Starcraft, Warcraft Ш, FIFA series games, CounterStrike, Winning 11, Age of Empire 3, and Dead or Alive.

Competition to win audiences among broadcasters already became fierce. It’s important to keep in mind that corporate sponsorship is involved as well, allocating millions of dollars in prizes and ad revenue.
Professionals and amateurs will gather at Seoul for the national qualifiers of the World Cyber Games (WCG) Aug.5-6. Organized by an affiliate company of Samsung Group, it has been the premiere international computer and video gaming festival since 2001. At the World Cyber Games (WCG), gold medal winning gamers bring in as much as $80,000 per tournament. The Olympic of video games was inaugurated in 2000 in Seoul, and now hosts players from sixty-seven nations. This year’s grand finals will be held at the F1 racing track of Monza, in northern Italy, in October, for the first time in Europe.

No comments:
Post a Comment